Private browsers are gaining popularity as more of our online activity is tracked and shared, but these browsers are just one important element of an effective online privacy strategy.
Let’s take a closer look at the best browsers for privacy and the tools and practices that make up an optimized, secure, and private browsing experience.
What makes a web browser private?
Private browsing or incognito browsing refers to a browsing mode where history is not tracked, and cookies are automatically deleted each time you exit the browsing session. Although history is not stored on the browser in private mode, the internet service provider (ISP) continues to track the sites you visited and your location based on your IP address.
Using a virtual private network (VPN) with private browsers enhances privacy by preventing the IP address from being tracked.
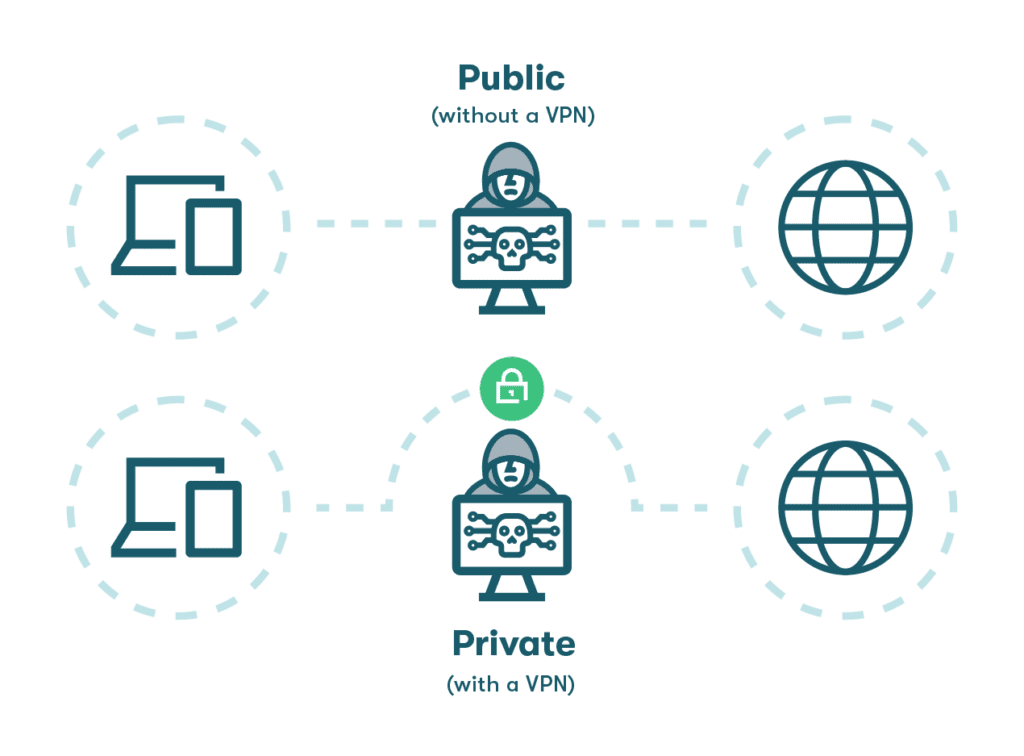
Why is secure web browsing important?
A new cyberattack is launched every 39 seconds around the world. Secure internet connections use the HTTPS protocol to encrypt data transmissions, scrambling data into a format that is unrecognizable and unusable for hackers. Encrypted internet browsing and website authentication practices safeguard user identity and prevent unauthorized access, while secure WiFi networks prevent data intercepts.
These elements combine to prevent cybercrimes and provide users with an enjoyable, private, and worry-free browsing experience.
Risks of unsecured browsing
In general, an unsecured browsing session is a browsing session that isn’t protected by encryption. Your browser is the engine behind every internet connection, so the security features of your go-to browser should be optimized to protect you from:
- Theft of sensitive information: Without the benefit of a secure, encrypted connection, hackers can intercept your online communications using tactics like man-in-the middle attacks. HTTPS and a VPN can provide protection for data in transit. The web browser must also be secured to prevent information like passwords saved on browsers from being exposed in a data breach since the built-in credential managers included with some major web browsers provide easy access to unencrypted password lists.
- Interception of private information: WiFi networks in public settings like hotels, airports, and cafés are often unsecured. Joining public networks without a VPN can put private information like form inputs, emails, and chats at risk. Your operating system will usually provide a warning like a conspicuous exclamation point symbol to let you know when the connection is not secure. Similarly, your web browser will warn you when you’re visiting an unsecured website, although it may not always prevent you from doing so.
- Expanding your passive digital footprint: Digital footprints are the impression of your identity left behind each time you use the internet. Unlike social media postings, blog posts, and other active footprints, passive footprints are usually left behind without our awareness and include browsing history data and IP address activity that can be leveraged for targeted advertising campaigns.
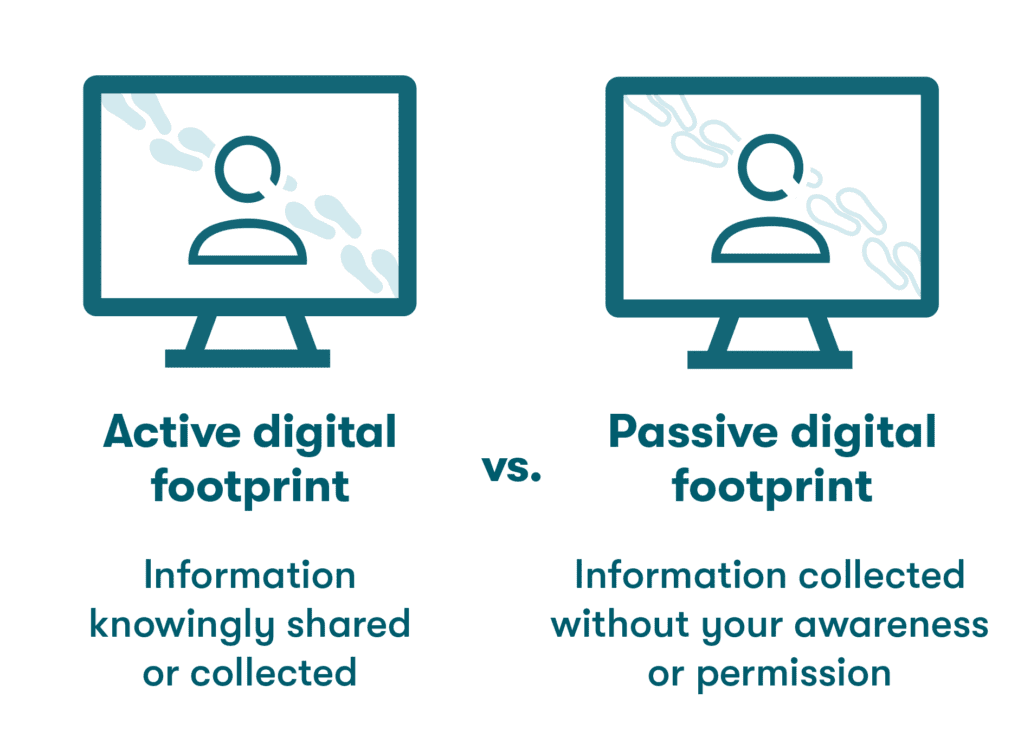
Best browsers for privacy
Many outstanding options have been developed to create a private browsing experience, with more entering the market all the time. The most secure browsers that don’t track your activity include:
- Brave. This Chromium browser blocks third-party ads, cookies, and trackers by default and includes an optional VPN, social media blocking, and partitioning of your data, among other security features. Since Brave does not track your searches or clicks, your data can never be shared with third parties.
- Tor. The Tor browser is an open-source platform that allows users to search and visit websites anonymously. The Tor deep web search engine was originally developed by the U.S. government to protect whistleblowers and circumvent surface web censorship. Traffic is relayed and encrypted three times as it passes over the Tor network, and each website you visit is isolated so that third-party trackers and ads can’t follow you.
- Firefox. Mozilla Firefox is a free, open-source browser developed by Mozilla Corporation in 2002. Firefox includes a popular private browsing feature that can be selected on demand or set as the default mode. Firefox supports private browsing by preventing third-party tracking techniques like cross-site tracking cookies and offers optional email breach monitoring and a VPN.
- DuckDuckGo. Founded in 2008, DuckDuckGo offers several products that help people improve their online privacy, including a privacy-focused search engine of the same name. Since its inception, DuckDuckGo has provided their search engine and other products to customers for free. In addition to their own proprietary browser, they also provide an extension that allows the search engine to be used with major browsers such as Chrome, Edge, and Firefox.
Add a credential manager to the most secure browser for ultimate privacy
Deciding on the most secure internet browser out of the four above is primarily a matter of personal preference since each option offers many unique features and benefits. While some products are only available as browser extensions, others include a wide range of privacy protection and security options within a full web browser platform.
The most secure browser option is one that enables private browsing and doesn’t encourage you to save passwords and other sensitive data in the browser itself. Such unencrypted data storage is a major security risk.
Tips for securing your web browsing
A truly secure browsing experience takes the benefits of the best incognito browser to another level by deploying a few readily available cybersecurity tools and practices:
- Use a VPN: A VPN is a must-have security tool when browsing on public WiFi networks, and it also brings some additional privacy and data protection benefits. When you use a VPN, even your ISP can’t see what websites you visit, apps you use, or the data you send and receive. A VPN also overcomes any content blocks based on geography.
- Erase passwords from your browser: Storing passwords in your browser isn’t a safe practice, so it’s a good idea to erase passwords from your browser so they won’t be exposed in the event of a cyberattack. It’s easy to migrate your saved passwords to a credential manager with a secure, encrypted storage vault and disable the password-saving feature on your browser.
- Use a credential manager browser extension: An extension (similar to a plugin) is a small program you can download to add features to your browser. By installing the Dashlane browser extension, you instantly make any browser more secure by encrypting and saving your logins and other data safely as you browse the web. You can view, copy, and generate passwords directly in the extension pop-up.
- Manage your digital footprint: Data retention policies for browsers, ISPs, and retailers make it difficult to delete your digital footprint entirely, but you can minimize and control the traces you leave behind by deleting cookies regularly, monitoring your social media accounts, and deactivating old email services. You can also query your own name to keep tabs on your online presence.
- Run antivirus software: Malicious software (malware) is any type of intrusive software that is intended to interfere with a computer’s function. Dangerous malware types like spyware and ransomware can invade your privacy or even extort money. Antivirus software protects you from these threats by continually quarantining and removing malicious files from your computer or device.
- Keep software updated: Web browser updates often include improvements to encryption protocols and security patches, so they should never be put off or ignored. Software updates ensure system vulnerabilities are addressed quickly to reduce the effectiveness of hacking tactics.
- Use encryption: The centuries-old practice of encryption has become an essential tool for password, website, and email security by scrambling digital information into an unrecognizable format that thwarts hacking attempts. Dashlane uses AES-256 encryption, widely accepted as the strongest encryption type available, to protect your private information.
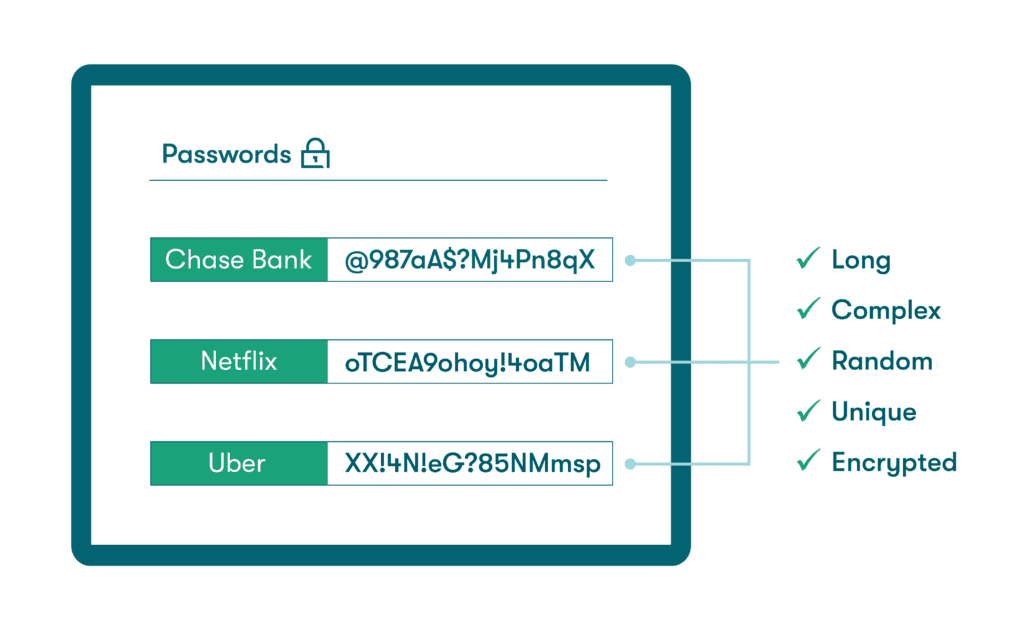
- Create strong, unique passwords: A strong password includes a random mixture of uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters, and it’s at least 12 characters long. Identifying information like your name and address should always be left out. Password safety also means avoiding habits like reusing passwords or sharing them through unsecured methods like text messages or Slack.
How Dashlane makes browsing more secure
In addition to intuitive password generation and customizable autofill that prevents you from logging in to unsecured websites, Dashlane provides strong AES-256 encryption, 2-factor authentication (2FA), and a Password Health score to track your weak, reused, and compromised passwords.
A VPN keeps your web browsing private, while our phishing alerts help prevent you from getting hooked by phishing messages, and Dark Web Monitoring scans the depths of the internet for your compromised credentials.
Our patented zero-knowledge architecture ensures no one else (not even Dashlane) can access your unencrypted data.
References
- Dashlane, “Are Private Browsers Really Private + Tips for Secure Browsing,” March 2023.
- Dashlane, “Protect more than your passwords with a fast, reliable VPN,” 2023.
- Zippia, “30 Crucial Cybersecurity Statistics, Data, Trends, and More,” June 2023.
- Dashlane, “7 Business WiFi Security Best Practices To Protect Your Company,” June 2023.
- Dashlane, “What Is Encryption?” March 2019.
- Dashlane, “Why Employees Shouldn’t Let Browsers Save Their Passwords,” March 2021.
- OSX Daily, “Traveling? Beware of Unsecured Hotel Wi-Fi Networks,” July 2022.
- Dashlane, “What Is a Digital Footprint and Why Is It Important?” August 2023.
- Brave, “Search Without a Trace,” 2023.
- Dashlane, “The Dark Web Iceberg Explained In Simple Terms,” June 2023.
- Tor Project, “Browse Privately Explore Freely,” 2023.
- Mozilla, “Get the browsers that put your privacy first — and always have,” 2023.
- DuckDuckGo, “One supercharged app, multiple types of privacy protection,” 2023.
- Dashlane, “Why Do You Need a VPN? Don’t Miss These 3 Key Benefits,” August 2020.
- Dashlane, “How to Erase Saved Browser Passwords: Step-by-Step Guide,” November 2022.
- Dashlane, “How to Prevent Ransomware Attacks on Your Devices,” March 2023.
- Security.org, “Do You Still Need Antivirus?” May 2023.
- Dashlane, “Why You Should Keep Your Apps Updated,” March 2022.
- Dashlane, “Putting Security First: How Dashlane Protects Your Data,” October 2023.
- Dashlane, “How Strong Is Your Password & Should You Change It?” August 2022.
- Dashlane, “A look at Password Health Scores around the world in 2022,” 2022.
- Dashlane, “These New Alerts Notify You When Something’s Phishy,” September 2023.
- Dashlane, “Dark Web Monitoring: Your Employees Are Likely Using Compromised Passwords,” July 2022.
- Dashlane, “Security Terms 101: What Zero-Knowledge Architecture, Encryption, and More Really Mean,” June 2023.
Sign up to receive news and updates about Dashlane
Related articles