Managing numerous, complex passwords can be overwhelming in today's digital landscape, where data breaches are all too common. Secure, reliable password managers simplify this task and fortify your digital defenses, ensuring your personal and business data is much more secure.
So, how exactly do password managers achieve this?
What is a password manager?
A password manager is a type of software you can use to generate, store, and autofill strong passwords, along with other frequently used information, such as credit card numbers. With the help of a password manager, you only need to remember one master password to access your encrypted virtual vault.
Although most popular browsers include a password manager with basic functionality, only a high-quality, third-party password management app offers features like a VPN, encryption, and 2-factor authentication that provide strong security and added convenience.
What a good password manager does
A password manager bolsters your digital security by creating robust, unique, and complex passwords for your online accounts. But what does this mean for you on a day-to-day basis?
Here's a closer look at the functionality that makes a password manager indispensable:
1. A zero-knowledge system
This security feature means that all your data is encrypted on your device before it reaches the password manager's server. This means even the service providers can’t see or access your sensitive information. It's like having a personal vault that only you know the combination to.
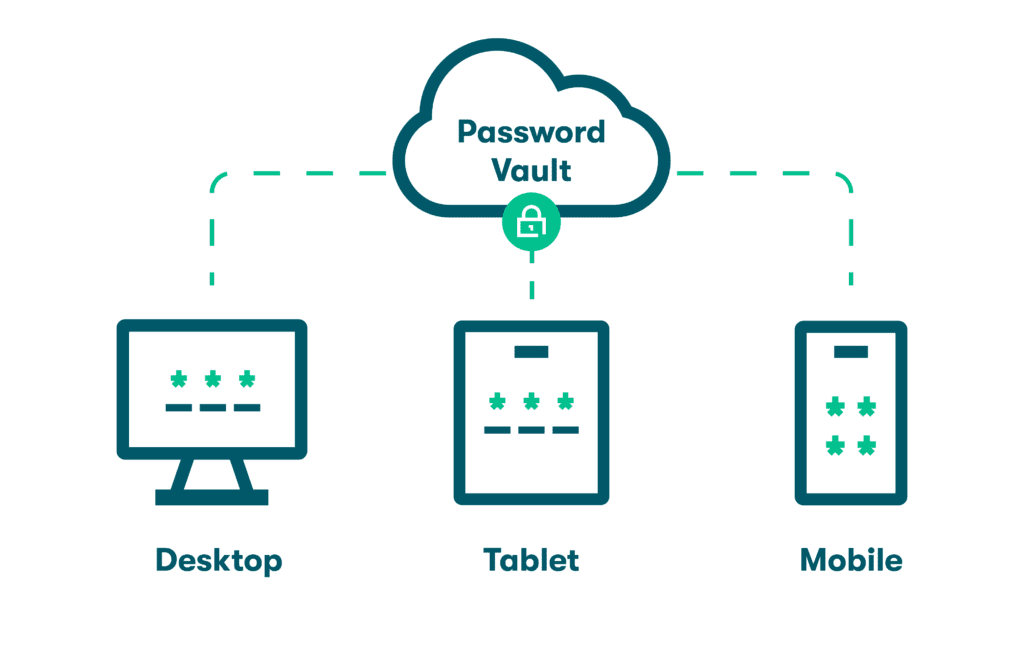
2. Device syncing
Managing passwords across multiple devices can be a hassle. Cloud-based password managers simplify this by syncing your passwords across all devices and operating systems in real time. Whether you’re using your laptop, smartphone, or tablet, your passwords are consistently accessible and up-to-date.
3. Password sharing
Need to share your Netflix or Wi-Fi password securely? Password managers use encryption to allow you to share passwords safely. This means you can give access without exposing your passwords in plain text, keeping your logins secure even when they're shared.
4. Dark Web Monitoring
The internet’s underbelly is vast, and data breaches are unfortunately common. Dark web monitoring involves scanning through billions of records on the dark web to see if your personal information is being traded or sold. If anything is found, you’ll be alerted immediately, allowing you to take proactive steps to secure your accounts.
5. Security alerts
If a website you use suffers a data breach, a good password manager will notify you. This prompt alert allows you to change your password before anyone exploits your information.
6. Single sign-on (SSO)
This feature allows you to log in once to securely access multiple platforms or apps. It’s a way to streamline your online activities without sacrificing security, making it easier for you to manage multiple accounts using a single authentication process.
7. A virtual private network (VPN)
For those frequently using public or unsecured Wi-Fi, a VPN integrated into your password manager can shield your online activity. By hiding your IP address, your browsing is private and secure from prying eyes.
What a password manager doesn’t do
Although the useful features incorporated into high-quality password management software continue to expand and improve, there are still a few things they don’t do, including:
- Completely prevent hacks and malware: Password managers aim to protect passwords and other sensitive data—after all, 61% of data breaches involve compromised logins—but cybercriminals have other ways of conducting cyberattacks. Adding 2-factor authentication (2FA) or multifactor authentication (MFA) is a good way to raise the security bar even higher.
- Monitor or control your browsing habits: Using an independent password manager in your browser doesn’t require you to share your personal information or browsing history. Zero-knowledge encryption means just that: your password manager doesn’t need to collect or monitor your information to keep you secure.
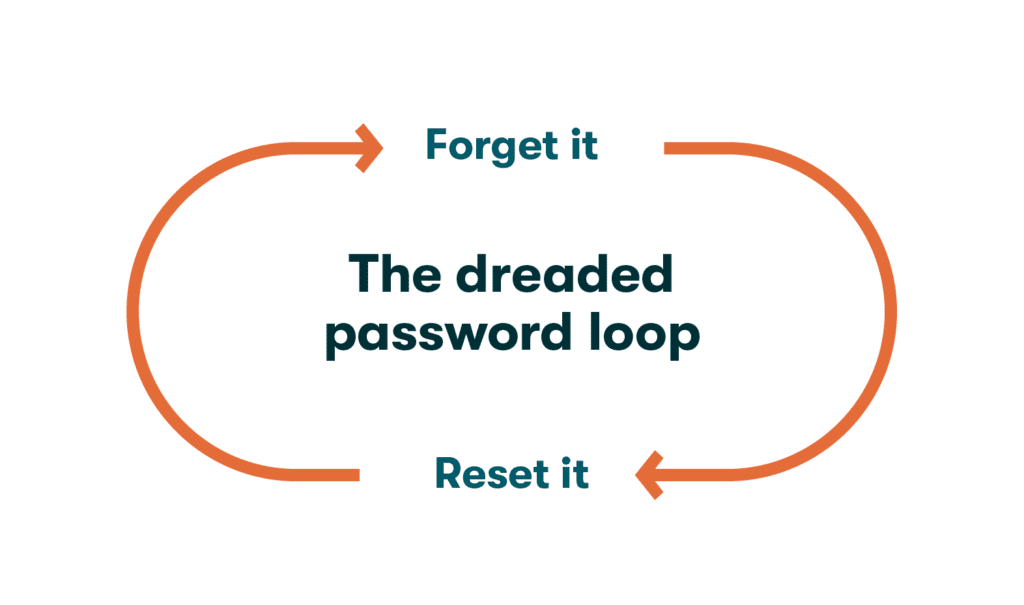
- Add more computer tasks or keystrokes to your busy day: In fact, it’s quite the opposite. Convenient, user-friendly autofill eliminates many data entry tasks, including the extra time spent creating, searching for, and resetting passwords.
Other types of password management software
In addition to independent password managers like Dashlane that work through browser extensions and apps, there are three other types of password managers available:
- Browser-based: Built-in password managers are included with many leading internet browsers. Unfortunately, many of these password managers favor convenience over security. A lack of data encryption is one of several security drawbacks of built-in web browser password managers.
- Stateless/token based: This type of password manager uses an external USB device or a code sent to a device app to unlock your account. Passwords are re-generated each time you log in with the token. If you lose or break the device, you also lose access to your accounts.
- Locally installed software: Independent password managers are sometimes installed locally rather than using an external cloud-based format. Passwords are stored and encrypted on each device individually. However, you run the risk of losing your passwords and data if your device is lost, stolen, or broken.
Setting up a password manager
Of course, all password managers vary in the time and effort required to get up and running. Dashlane has developed software that’s easy to set up and use. Once Dashlane is installed, a web page will automatically direct you through the account setup process. You can then begin auto-generating new account passwords you wish to autofill over time. You can also turn on instant syncing between your devices and view your Password Health score to monitor your password strength and security.
Tom Kowalkowski, IT Technician, Sheehan Nagle Hartray Architects
Password manager FAQs
1. What is the purpose of a password manager?
A password manager makes it possible for individuals or businesses to store, create, and manage all their passwords from one secure app. Automatic password generation and encryption eliminate the need to create and remember complex passwords for each account. A good password manager increases both security and efficiency.
2. Do password managers work on multiple devices?
The short answer is YES. Most cloud-based password managers make it easy to sync your passwords between various devices. Dashlane stores your encrypted password information in a secure cloud location, so you can access passwords and make updates from any of your computers, smartphones, or other devices. Locally installed browser management software doesn’t offer this convenience.
3. How are passwords encrypted?
Encryption, or the art of hiding information in an unrecognizable format, dates back to the ancient Egyptians. Modern computer data encryption takes plain text data and scrambles it into a format called ciphertext. Dashlane’s encrypted password manager uses AES-256 encryption, widely accepted as the strongest encryption method available, to scramble your passwords, even before they leave your computer or device to go to our servers.
4. What is a password vault?
A password vault stores all your secret password information. Locally installed password managers store your data on the hard drive or device memory, leaving it accessible to others if your device is lost or stolen. Built-in browser password managers back up your information on their servers but also provide an unencrypted list of all the passwords you’ve stored, which can leave them vulnerable to a breach. However, Dashlane’s zero-knowledge architecture means we only store encrypted password data on secure, regularly audited Amazon AWS-hosted cloud servers.
5. What is a browser extension?
A browser extension is a plug-in for your favorite browser that adds additional features. The Dashlane browser extension helps you integrate secure, independent password management into your daily routine. Once you set up Dashlane in your browser, Dashlane will help you save your logins. Keep in mind that using a browser extension in conjunction with a premium password management app like Dashlane is entirely different from (and superior to) relying on a native browser password manager alone.
What Dashlane does for password management

Installing new software to help you manage and remember passwords might sound like a contradiction: Just one more thing to slow you down on the path to value-added work, right?
Wrong!
Dashlane’s browser extension and mobile app provide an antidote to the inefficiency of our multi-tasking, multi-password lives. Secure password sharing also makes it easier to collaborate with virtual colleagues all over the world.
Here are just a few of Dashlane’s key features for business and personal users:
- Single sign-on (SSO) integration
- SCIM directory sync
- Built-in 2-factor authentication
- Dark Web Monitoring
- VPN
- Password Health score
- AES-256 encryption
Hackers go to great lengths to steal passwords and unlock confidential information. Secure, user-friendly password managers like Dashlane are among the most effective tools available to boost cybersecurity while helping you log in to the accounts you need more easily.
Sign up to receive news and updates about Dashlane
Related articles