How To Prevent and Respond to Data Breaches
The average cost of a data breach globally in 2023 was $4.45 million, a 15% increase over 3 years. Organizations not only face financial losses but also reputational damage. For businesses striving to prevent or recover from a data breach, knowing the right course of action can be challenging. Let’s explore how to prevent a data breach and mitigate these risks.
What is a data breach?
A data breach is a security incident where someone accesses sensitive, confidential, and protected data without authorization. It occurs when data protection security measures are violated. These violations can be accidental or intentional, but they’re often orchestrated by cybercriminals motivated by financial gain, espionage, or terrorism.
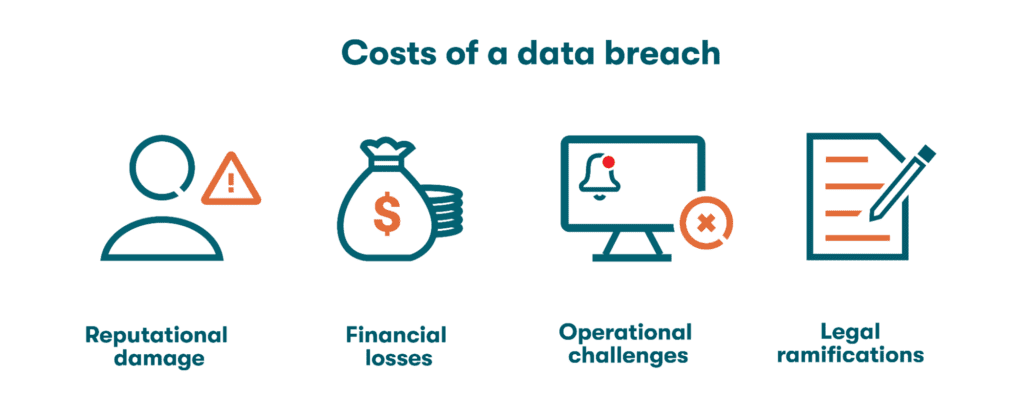
The loss or theft of sensitive information, ranging from financial credentials to intellectual property, can have far-reaching consequences. These may include reputational damage, financial losses, operational challenges, and legal ramifications, in addition to resources spent on investigations and remedies.
Many cybercriminals tend to leak such sensitive information on the dark web, an anonymous part of the internet that’s become a breeding ground for malicious activities. There, anonymous individuals can purchase stolen logins, bank account credentials, and company data in just a few clicks.
How does a data breach happen?
Data breaches typically result from system vulnerabilities and lax user behaviors that hackers exploit. The increasing reliance on technology often prioritizes convenience over security, leading to a rise in data breach incidents. Some of the most common ways data breaches occur include:
- Accidental breach (internal and third parties): This occurs when an individual inadvertently triggers a cybersecurity breach by falling prey to phishing attacks, using personal devices in unsecured ways, or using weak passwords. Unintentional access to a coworker's device and viewing their sensitive information (such as during a screen share) also constitutes a data breach, even if the viewer doesn't share the information or have malicious intent.
- Malicious insiders: A malicious or criminal insider is typically an employee or contractor who exploits their access to deliberately disclose sensitive company data to unauthorized third parties or other employees. Their actions are usually driven by personal gain or the intention to harm the organization and profit from the breach.
- Lost or stolen devices: Misplacing any physical device, such as an unsecured laptop or mobile phone, can pose a significant risk. These devices may contain unencrypted confidential data that cybercriminals could potentially exploit. Hence, employees must take precautions to secure their devices where bad actors could access company data.
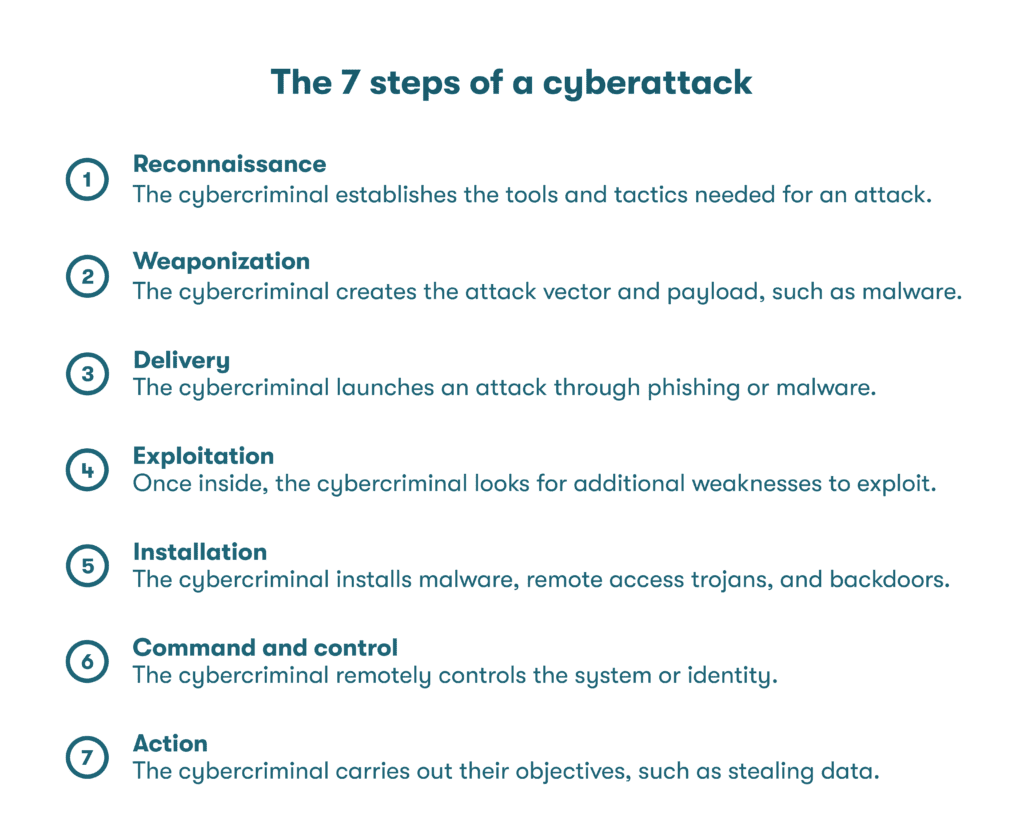
- Cyberattacks: Experts have determined that cyberattacks typically unfold over seven steps, starting with thorough research to identify vulnerabilities within an organization’s digital infrastructure. Cybercriminals gain unauthorized access to the system by exploiting security loopholes, which enable them to breach and steal valuable information for malicious purposes.
The rising popularity of cybercrime has made cybersecurity more important than ever. Learn about the different types of cyber threats to be aware of and defend against.
How to prevent data breaches
Implementing preventive measures such as using prevention tools and following robust security practices are the best ways to prevent data breaches. The following methods will help you understand how to avoid data breaches and minimize their impact.
- Create a cybersecurity policy, including an incident response plan
A comprehensive cybersecurity policy helps an organization respond to data breaches, speed up breach detection and containment, and take steps to prevent future mishaps. The policy details how the organization will maintain secure systems, enforce access protocols, and train employees on cybersecurity best practices. As part of this policy, an incident response plan (IRP) details the steps to take when a cyberattack occurs. And a password policy helps prevent cyberattacks by educating employees on the best practices and rules for password use with business accounts.
- Follow security best practices
Implementing best practices to prevent data breaches can effectively safeguard sensitive data and help mitigate the risks of breaches.
- Create and securely store strong passwords: Strong passwords that are unique, complex, and lengthy help prevent cyber criminals from hacking into your IT systems. The best place to store passwords is an encrypted password manager.
- Use a VPN: A virtual private network (VPN) encrypts your online activities, adding an extra security layer even if you’re using unsecured WiFi. VPNs can facilitate compliance with data protection regulations and company privacy policies. They prevent internet surveillance and data interception by cybercriminals who may be lurking on the same network, reducing the risk of data breaches.
- Turn on 2-factor authentication: 2-factor authentication or 2FA requires additional verification (usually a unique code sent to your mobile device) when logging in to accounts. 2FA makes it significantly harder for attackers to access sensitive data because even if they manage to obtain your password, they also need your device.
- Compartmentalize your network: You can isolate sensitive data from other systems or devices by segmenting your organization’s network into subnetworks. Separation helps minimize the exposure and potential damage if one area of your network is compromised.
- Single sign-on (SSO): SSO allows users to access multiple apps and systems using a single set of credentials. It simplifies access management by allowing users to authenticate once and access multiple systems, reducing the burden of managing multiple usernames and passwords.
With SSO, IT admins can easily allow and revoke access, enabling timely and secure access control to company systems. SSO also strengthens security through strong authentication measures, simplifies auditing and reporting, and integrates with Identity and Access Management (IAM) software for centralized control over user permissions and supervision.
- Leverage data breach prevention tools
Understanding how to protect against data breaches involves leveraging prevention tools, which act as the first line of defense when cyber criminals attempt to hack into IT systems.
Here's a list of the most effective solutions to data breaches to include in your arsenal:
- Endpoint security solutions: Endpoint security refers to protecting user devices, such as desktops, laptops, and mobile phones, from cyber threats. It focuses on securing these devices and the data they access, store, or transmit, regardless of their location or network connection.
Companies like Crowdstrike and Cloudflare specialize in endpoint security solutions that aim to prevent, detect, and respond to various data breaches. For example, Crowdstrike's Falcon platform combines AI, machine learning, and behavioral analysis for advanced endpoint protection, offering continuous monitoring, threat hunting, and incident response services. Cloudflare, on the other hand, primarily focuses on web security and performance solutions but also provides endpoint security features to protect devices connecting to their network from web-based threats.
- Password manager: A password manager can help avoid data breaches by organizing and protecting your credentials across multiple accounts and devices. It securely generates, stores, and autofills passwords, reducing the risk of weak or reused passwords that can be easily compromised. Advanced password managers, like Dashlane, offer additional layers of security in the form of encryption, 2FA, and a VPN.
- Security information and event management (SIEM) software: SIEM tools provide real-time monitoring and analysis of events, helping identify and respond to security incidents promptly. By collecting and correlating data from various sources, SIEM software enhances threat detection, preventing data breaches by alerting security teams about suspicious activities or anomalies.
- Intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS): These systems monitor network traffic, detect potential threats, and actively prevent unauthorized access or malicious activities. IDPS can identify and block suspicious behavior, such as repeated attempts to access sensitive data, reducing the chances of a successful data breach.
- Promote employee training and awareness
Educating employees about cybersecurity risks and how to identify and respond to threats is a vital preventive measure. For example, regular communication should remind them about the risks of clicking on suspicious links or email attachments from unfamiliar sources. Training and a culture of security ensure every individual understands their daily role in protecting company data.
- Conduct vulnerability assessments
Running vulnerability assessments can proactively identify system, network, and app weaknesses and vulnerabilities. By regularly assessing and addressing these vulnerabilities, organizations can implement necessary security measures and patches to close potential entry points for hackers.
- Update software and security patches regularly
Software updates and patches include fixes for known vulnerabilities and security weaknesses. By promptly applying these updates, organizations ensure their systems are equipped with the latest security measures.
Now that you know how to prevent a data breach, let’s learn how to respond to and contain a data breach.
How to respond to a data breach
With the number of data breaches rising almost every year, no company is immune. However, prepared companies can mitigate the situation as swiftly as possible. Follow the steps below to respond quickly and effectively to a security incident.
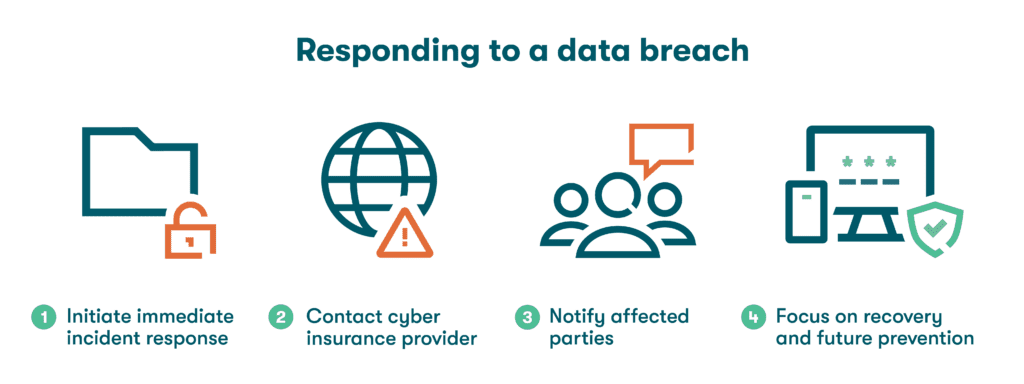
- Initiate immediate incident response actions
- Detect the breach
Actively monitor network logs, security alerts, and abnormal activities to identify signs of a data breach. Intrusion detection systems and security tools can help identify unauthorized access or suspicious behavior.
Timely detection of a data breach is crucial to containing the damage. If a breach goes unnoticed, the intruder may be able to access other areas of a company network, monitor business activities, or sell more private info on the dark web. Many high-profile companies have experienced breaches that were discovered months or years later, such as the Yahoo breach in 2013, which was detected after four years, and the Equifax breach in 2017, which remained undetected for months.
- Contain the breach
Once a breach is detected, the goal is to minimize its spread and prevent additional data exposure or damage. First, isolate the affected systems and disconnect them from the network. To limit the damage, you can also implement stricter temporary measures, like firewall restrictions, access controls, and network segmentation.
- Gather evidence and analyze
Collect and preserve evidence of the breach for an in-depth analysis. In the case of a major data breach, most companies choose to hire a reputable third-party cyber forensics team to perform this analysis.
A comprehensive data breach analysis involves: - Documenting the timeline of events: This documentation serves as a reference for the investigation and helps establish a clear understanding of the sequence of events.
- Capturing system logs: They contain valuable information about user access, network traffic, and system behavior, which can provide insights into the breach and help reveal the attacker's methods.
- Analyzing the attack methods and entry point: Various methods like network traffic analysis, forensic imaging, and malware analysis can be used to review the attack methods and determine the entry point of the breach.
This information is crucial for understanding the scope of the breach and implementing appropriate remediation measures. It also helps implement more robust security mechanisms to prevent future breaches of a similar nature.
- Eliminate all causes of the breach
Use all the gathered evidence to identify and address the root causes that led to the breach. Investigate existing weaknesses by conducting penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and code reviews to uncover potential security flaws. Then analyze the security controls and determine any security gaps that could have been exploited by the attackers that need to be patched up.
During your investigation, consider the human element, too. Review employee activity, awareness, and training to identify any lapses in security practices that could have led to social engineering attacks or insider threats.
Once all the causes are identified, take immediate action to remediate them by patching software, updating systems, and applying security patches to fix known vulnerabilities.
- Contact your organization’s cyber insurance provider
Data breaches can have severe financial consequences, particularly for small businesses with limited resources. Cyber insurance covers different types of cyberattacks and can help offset costs such as legal expenses, data recovery, and software repairs. Contact your cyber insurance provider for guidance following a breach.
- Notify affected parties
It can be a complex process to notify affected parties, such as authorities, employees, third parties, vendors, and customers, based on various regulations. It’s usually best to take proactive control of your company's reputation by being the first to disclose the breach to the public. By doing so, you can shape the narrative and ensure accurate information about the incident is shared, preventing speculation and fear-mongering from external sources.
Data breach notifications must be provided through proper channels to comply with applicable laws. Notifications typically cover breach details, steps taken, and recommended actions for recipients. Failure to fulfill notification requirements may result in penalties, legal troubles, reputational damage, and even the loss of certain business privileges.
- Focus on recovery and future prevention
Recovery from a data breach involves conducting thorough security audits to assess vulnerabilities and demonstrate due diligence. Engaging external experts who can provide objectivity and expertise in analyzing systems and proposing effective fixes and policies can be a worthy investment.
To prevent future breaches, businesses should adopt proactive, layered defense approaches that include advanced security measures (like breach prevention best practices and tools), conduct regular training and awareness programs, enforce robust security policies, and maintain incident response plans.
How Dashlane helps businesses prevent data breaches
Dashlane strives to foster a culture where privacy and security are made simple. Dashlane’s standard features, including a Password Generator, Password Health score, and 2FA, deliver enhanced user authentication and access management.
All customer data, including usernames, passwords, notes, and metadata, are encrypted with Dashlane. Dashlane uses Argon2, a highly secure hashing algorithm that generates a strong AES 256-bit key for data encryption and decryption. Crowned as the winner of the Password Hashing Competition, it’s considered to be one of the most secure hashing algorithms. Coupled with zero-knowledge architecture, no one, not even Dashlane, can access your data.
Learn how Dashlane helps organizations stay ahead of data breaches with real-world case studies. In one comeback story, JD+A recovered compromised passwords, secured their data, and implemented a solution to help build trust with their clients.
References
- IBM, “Cost of a data breach 2023,” 2023.
- Avast, “What is a Data Breach?” March 2021.
- Kaspersky, “How Data Breaches Happen.”
- CFI, “Data Breach,” March 2021.
- Security Metrics, “Incident Response: 10 Things to Do if You Have a Data Breach.”
- IBM, “What is SIEM?”
- Microsoft, “What is data loss prevention (DLP)?”
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), “Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems.”
- UpGuard, “How to Create an Incident Response Plan (Detailed Guide),” January 2023.
- NPR, “Every Yahoo Account That Existed In Mid-2013 Was Likely Hacked,” October 2017.
- CSO, “Equifax data breach FAQ: What happened, who was affected, what was the impact?” February 2020.
- Dashlane, “Why Every Employee Device Should Be Secured,” May 2021.
- Dashlane, “11 Cyber Threats To Be Aware of & Defend Against,” April 2023.
- Dashlane, “How To Create a Small Business Cybersecurity Plan That Works,” February 2023.
- Dashlane, “6 Tips to Create Strong, Secure Passwords in a Digital World,” March 2023.
- Dashlane, “Why Do You Need a VPN? Don’t Miss These 3 Key Benefits,” December 2022.
- Dashlane, “How a Password Manager Protects You and Your Data,” October 2022.
- Dashlane, “How to Create a Culture of Security,” March 2022.
- Dashlane, “Interview With a Hacker: Rachel Tobac Tells You How to Defend Yourself From…Well, Her!” March 2021.
- Statista, “Annual number of data compromises and individuals impacted in the United States from 2005 to 2022,” January 2023.
- Dashlane, “6 Reasons Why Your Business Needs Cyber Insurance,” November 2022.
- Dashlane, “Putting Security First: How Dashlane Protects Your Data,” January 2023.
- Dashlane, “A Comeback Story: How JD+A Spotted Their Compromised Passwords and Secured Company and Client Data,” March 2022.
- Dashlane, “How to Shine a Light on the Dark Web,” June 2022.
- Dashlane, “How Strong Is Your Password & Should You Change It?” August 2022.
- Dashlane, “The 7 Steps of a Cyberattack,” April 2023.
- Dashlane, “Creating a Password Policy Your Employees Will Actually Follow,” July 2022.
- Dashlane, “A Beginner’s Guide to Two-Factor Authentication,” August 2022.
- Dashlane, “Dashlane's Security Principles & Architecture.”
- Dashlane, “A Guide To External Security Threats in 2023,” May 2023.
- Dashlane, “Why You Should Keep Your Apps Updated,” March 2022.
- IT Governance USA, “Data Breach Notification Laws by State,” 2018.
- Password-hashing.net, “Password Hashing Competition,” 2019.
- Dashlane, “IAM: 3 Letters That Will Drastically Improve Your Organization’s Cybersecurity,” August 2022.
Sign up to receive news and updates about Dashlane
