7 Ways to Determine if You Have a Strong (or Weak) Password
Strong passwords protect against hacks, identity theft, and other cyber threats, but how do you know if your passwords are good enough? The definition of a strong password is more science than art, so there’s no need to guess. We break down the characteristics of strong and secure passwords and explain how to easily assess and improve the strength of your own passwords.
Want to learn more about using Dashlane Password Manager at home or at work?
Check out our personal password manager plans or get started with a free business trial.
What is a strong password?
Hackers use many different approaches to compromise passwords, ranging from social engineering (phishing) to advanced computer algorithms that guess at passwords and usernames. This can make deciding what’s a good password and what isn’t feel a bit subjective.
A strong password is one that can withstand diverse cyberattacks and is likely to remain secure as long as it remains private. Achieving this goal is easier when you follow a few password creation best practices and password hygiene habits.
A password generator automatically creates strong passwords based on your guidelines to meet different sites’ unique requirements. Try our free online tool to generate strong, random passwords.
Characteristics of a strong password
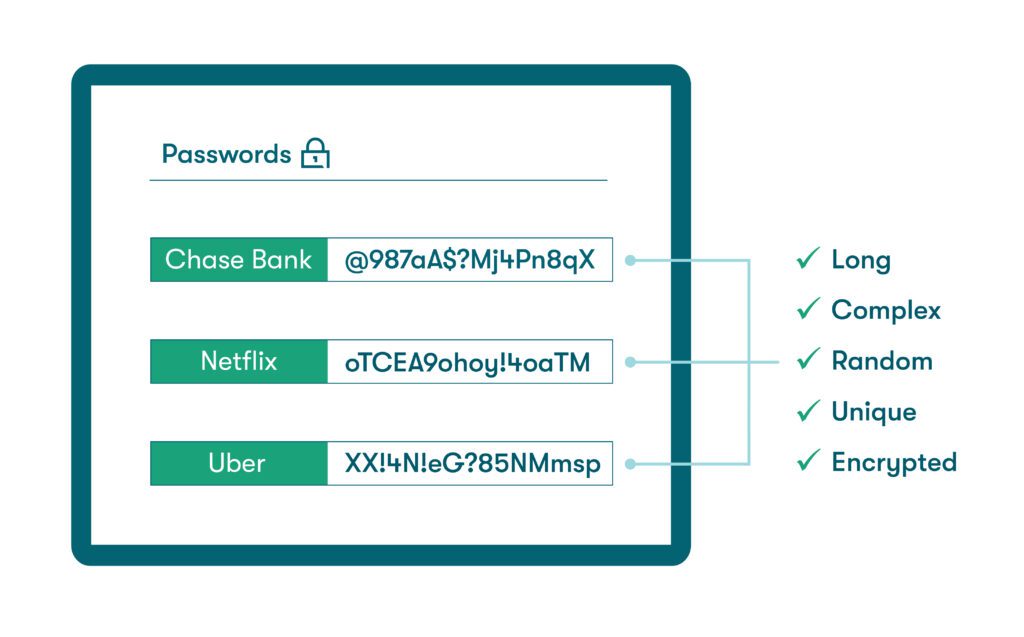
The difference between strong and weak passwords can be the difference between being protected and getting breached. Cybersecurity experts’ strong password definition includes the following characteristics:
- Long: According to the Center for Internet Security (CIS), length is the most important aspect of a good password. Sophisticated hacking tools can crack short (8 characters or less) passwords in less than three seconds. This time increases exponentially with each additional character. Not all experts agree on the ideal length, but increasing the number of characters from 7 to 12 makes passwords significantly more secure.
- Complex: A complex password includes a combination of uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Since there are only 10 numeric options and 52 alphabetic options (in addition to allowable special characters), mixing up password character types is essential.
- Random: Human nature often leads us to upcycle old passwords and use common phrases or personal info based on convenience and ease of memorization. Cybercriminals are aware of this familiar pattern, so being random on purpose is another important password characteristic.
- Unique: What is a unique password? This means a password is only used once and never reused for other accounts. The common habit of password reuse becomes a bonus for hackers when they hit on a login combination that unlocks many accounts simultaneously. Each new password should be created individually.
- Encrypted: Hiding information in an unrecognizable format is a practice that dates to ancient times (think coded letters and ciphers) and is now an essential password security practice in the digital age. Scrambling passwords through encryption makes them unreadable to cybercriminals and lessens the impact of a data breach. Dashlane Password Manager utilizes AES 256-bit encryption, widely accepted as the strongest encryption type available, to protect your passwords and other data.
Creating the ultimate password
What is a strong password example? Utilizing the basic characteristics of a strong password to their fullest extent yields something like this:
U6wjZ*PeU@rjTxVs
This long, complex, random, and unique password would take 1 trillion years to crack even with the best available hardware and software tools.
Seven ways to evaluate the strength of your password
You can use the rules and best practices that have evolved around strong password creation to evaluate your existing passwords and their attributes, including:
- Character count: How long does a password need to be? PCI password requirements developed to protect credit card transactions specify 7 or more characters. When you review the math, you’ll find that each character you add to a password doesn’t just double the entropy (complexity), it multiplies it many times over to make the password more secure. For example, increasing the number of characters from 7 to 12 raises the number of possible combinations from 8 billion to 95 quadrillion.
- Mix of characters: Our strong password example shows how mixing characters can make passwords more complex and harder to decode. Complexity requires you to think outside of the box by using capital letters within the password, not just the beginning. Mixing characters effectively also means steering clear of simple strings like 12345 or QWERTY that are far too easy to guess.
- Special character placement: Don’t special characters belong at the end of the password? Absolutely not! Since some authentication methods support the use of special characters and others don’t, adding a question mark or exclamation point at the end of an alphanumeric password is a common approach. This wastes a golden opportunity to create a more complex password by adding several special characters within the body of the password.
- Not commonly used: Cybercriminals stay up-to-date with the most commonly used passwords to improve their odds when they deploy password-guessing algorithms. With unimaginative and predictable passwords like Password, Qwerty, and 123456 topping the list, many of these commonly used (and hacked) passwords would be considered vulnerable even without the benefit of published lists.
- Omits personal information: When you include information like your name, address, or pet’s name in your password, it can be easier to remember and also more vulnerable. This personal information can often be found through social media accounts and other readily available sources. Personal information also includes things like favorite bands, vacation spots, and sports teams you may be inclined to include in your password.
- Check your password health score: Password health refers to the level of password security for any given user or group of individuals. The best password managers calculate your password health score based on the number of weak, reused, or compromised passwords in your portfolio. These features also tell you which accounts are most at risk and which passwords should be updated immediately.
- Use a password manager: The right password manager helps you identify weak passwords and replace them with strong, random, and unique passwords. Automatic password generation, an encrypted vault for secure password storage, and convenient autofill eliminate the need for password memorization and unsecure storage. A good password manager also makes it more convenient to create and maintain strong passwords.

How to create a strong, unique password
The strong password recipe isn’t hard to follow, but giving in to common password habits and creating new versions of originals is a familiar pattern. The password generator feature of a password manager takes the legwork and guesswork out of this important process, using advanced algorithms to instantly create long, random, and unique passwords for you. Once you have established these strong, secure passwords, your focus can shift to improving password storage and hygiene practices.
Dashlane Password Manager provides end-to-end password protection and is easy to set up and use. Learn more about our security-first password manager.
Other security tips for managing your passwords
Establishing strong passwords and eliminating weak ones is the first step toward improved password management and security. A few additional tools, tricks, and precautions will help you complete this journey to password safety.
- Change passwords only when necessary. How often should you change passwords? While there are no set rules, NIST guidelines explain why minor changes made during forced resets are easily predictable and of little value. For this reason, many companies are moving away from fixed 30/60/90-day reset intervals and relying on password managers instead. However, you should always update your passwords if you’ve been impacted by a data breach, shared passwords unsecurely, or used a public WiFi network without a VPN to route data transmissions through a secure portal.

- Don’t reuse passwords. Repeating old passwords is an easy habit to fall into, and a difficult one to break, since we’re inclined to create passwords that are easy to remember. Reusing passwords diminishes password security, because multiple accounts can be impacted if a reused password is compromised. Updating credentials becomes a long and laborious process if any of your reused passwords are exposed.
- Only share passwords securely. It can be difficult to avoid sharing passwords with friends, family, and coworkers for services like video streaming and online retail accounts. Unencrypted password-sharing methods like email, text messages, or Slack increase your vulnerability to hacks and data intercepts. The Dashlane encrypted sharing portal is a safe option for sharing passwords, files, or private messages with other Dashlane users.
- Monitor your password health: Keeping track of your password health helps you assess the strength of all your passwords regularly. It also encourages you to continue incorporating strong password characteristics while improving your cybersecurity profile over time. The Dashlane Password Health score provides a user-friendly dashboard to capture all of your important password metrics on one screen.
- Use 2-factor authentication. 2-factor authentication (2FA) uses a second credential, like a push notification or code sent through an app or text, to confirm user identity. 2FA should always be turned on when it’s available since it negates the impact of many common hacks. With 2FA protection, cybercriminals who buy or steal your password will also need to take possession of your device to overcome this valuable security practice.
- Store passwords securely. What is a secure password? To protect your passwords, you need to be sure no one else has (or can get) access to them. Even the strongest passwords are of no value if left exposed in an unsafe storage location like an open drawer, sticky note, or shared spreadsheet. The best way to store passwords safely is by using a password manager to create and store strong, encrypted passwords on secure external servers, where they’re always protected.
How Dashlane creates and protects strong passwords for you
Dashlane helps you generate and manage strong and secure passwords automatically. Convenient, customizable autofill boosts productivity without sacrificing security. Standard features including AES-256 encryption, a Password Health score, a secure sharing portal, and a VPN improve your cybersecurity and productivity at home, at work, and on the road.
Our Dark Web Monitoring scans the depths of the internet for your credentials and alerts you if your password information is detected, while our zero-knowledge architecture ensures that no one, including Dashlane, can ever access your unencrypted passwords and personal information.
Passwords may be woven into the fabric of our daily lives, but they originated with the ancient Roman army. We review where passwords have been, and where they’re headed, in A Brief History of Passwords.
References
- Dashlane, “7 Password Hygiene Best Practices to Follow,” February 2023.
- KimKomando, “Use this chart to see how long it’ll take to crack your passwords,” March 2021.
- Dashlane, “How Strong Is Your Password & Should You Change It?” August 2022.
- Georgetown University, “With Passwords, Size Matters!” 2023.
- Dashlane, “The Power of Unpredictable Passwords,” August 2020.
- Dashlane, “How Password Reuse Leads to Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities,” May 2023.
- Dashlane, “What is Encryption?” March 2019.
- Hive Systems, “Are Your Passwords in the Green?” April 2023.
- Dashlane, “A Complete List of PCI Password Requirements for Businesses,” June 2023.
- LMG Security, “How long should your password be? The data behind a safe password length policy,” January 2020.
- Dashlane, “10 Most Common Passwords of 2023 (Is Yours on the List?)” September 2022.
- Dashlane, “How To Remember Hard-To-Remember Passwords,” November 2022.
- Dashlane, “Password Management 101,” 2023.
- Dashlane, “Why You Need to Have Secure Passwords in 2023,” February 2023.
- Dashlane, “Resist hacks by using Dashlane's password generator tool,” 2023.
- Dashlane, “Top 10 Password Tips & Tricks to Protect Yourself,” February 2023.
- Dashlane, “How Often Should You Change Your Password for Online Accounts?” January 2023.
- Dashlane, “Protect more than your passwords with a fast, reliable VPN,” 2023.
- Dashlane, “7 Dangers of Sharing Passwords Without a Password Manager,” March 2023.
- Microsoft, “What is two-factor authentication,” 2023.
- Dashlane, “Dark Web Monitoring: Your Employees Are Likely Using Compromised Passwords,” July 2022.
- Dashlane, “A Brief History of Passwords,” 2023.
- Dashlane, “What Is Password Sharing & When Should I Use It,” February 2023.
Sign up to receive news and updates about Dashlane
