A Complete Guide to Asymmetric Encryption: Definition & Uses
When encryption was first used over two thousand years ago to encode wartime messages, no one could have imagined the role it would one day play in maintaining internet privacy and security. Today, many different symmetric, asymmetric, and hybrid encryption methods have been developed. Asymmetric encryption continually protects businesses and individuals from data theft and unauthorized access.
What is asymmetric encryption?
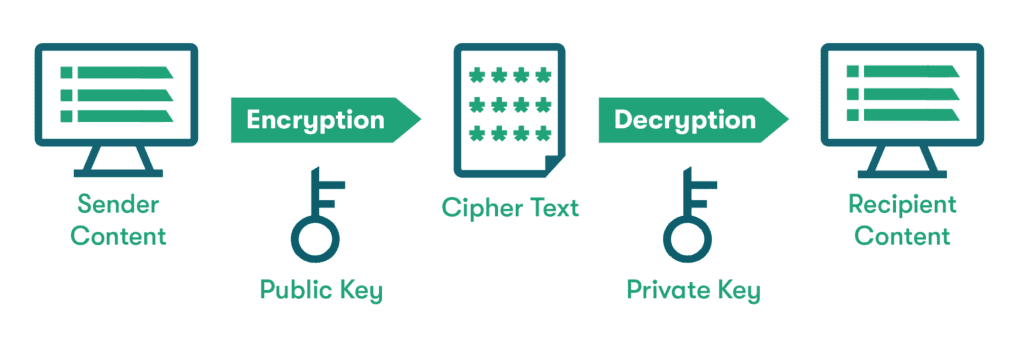
Encryption is a method used to scramble information to make it unreadable or unusable. With normal (symmetric) encryption, the same key used by the sender to encrypt (scramble) the data is used by the recipient to decrypt (unscramble) it. With asymmetric encryption, one key is used by the sender, and the recipient uses a different one. Think of it as a safe with independently locked doors on either side. This added feature makes asymmetric encryption more secure and less susceptible to hacking.
How does asymmetric encryption work?
Asymmetric encryption uses a method known as public key or asymmetric key encryption to create a public key-private key pairing. The public key only works for encryption, and the private key only works for decryption. A mathematical process called a cryptographic algorithm is used to generate these keys and link them together in a unique way for each key set.
Want to learn more about using a password manager for your business?
Check out Dashlane's password manager for small businesses or get started with a free business trial.
Where is asymmetric encryption used?
Asymmetric keys are a new concept for most of us, so it’s surprising to learn that asymmetric encryption is behind many common transactions and processes we take for granted. The important applications of asymmetric encryption include:
- Email security: Email encryption is used to prevent hackers from reading confidential messages, even if they successfully infiltrate the network. Most email providers use the standard encryption protocol called Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions or S/MIME. Using this method, public encryption keys are readily available for each email sender, but private keys are only provided to the recipient of each message. With over 300 billion email messages sent each year, safeguarding email security may be the most important asymmetric encryption example.
- Web security: When a web address contains the acronym HTTPS rather than HTTP, the trailing S stands for secure. This is also a sign that the connection is protected with asymmetric encryption rather than the standard encryption protocol followed by HTTP websites. Your web browser automatically locates the public encryption key when you visit an HTTPS website, then all information you send to the website is decrypted by its private key.
- Messaging apps: Messaging apps like Signal, Telegram, and WhatsApp rely on end-to-end encryption to ensure messages are scrambled from the time they leave the sender until they reach the recipient. Even the servers that process these messages are unable to decode them. This end-to-end scrambling is completed with asymmetric key encryption. Only the message recipients hold the private keys, and no session data logs are saved.
Dashlane has harnessed the power of cybersecurity innovations like data encryption, 2-factor authentication (2FA), and memory protection to keep the user experience as convenient and secure as possible. Find out more in our Security White Paper.
What are the benefits of asymmetric encryption?
Asymmetric encryption is an established, scalable solution for a variety of online applications. The benefits of asymmetric encryption include:
- Increased data security: Security benefits are provided through the additional steps of the asymmetric encryption process. The public encryption key can be shared with anyone, but the secret private key is only held by a single recipient. This means cybercriminals are unable to decode the messages they intercept. Asymmetric encryption algorithms also have larger key sizes (up to 4096 bits), making them harder to decode. These security features make asymmetric encryption ideal for highly secure internet transactions like online banking and virtual private networks (VPNs).
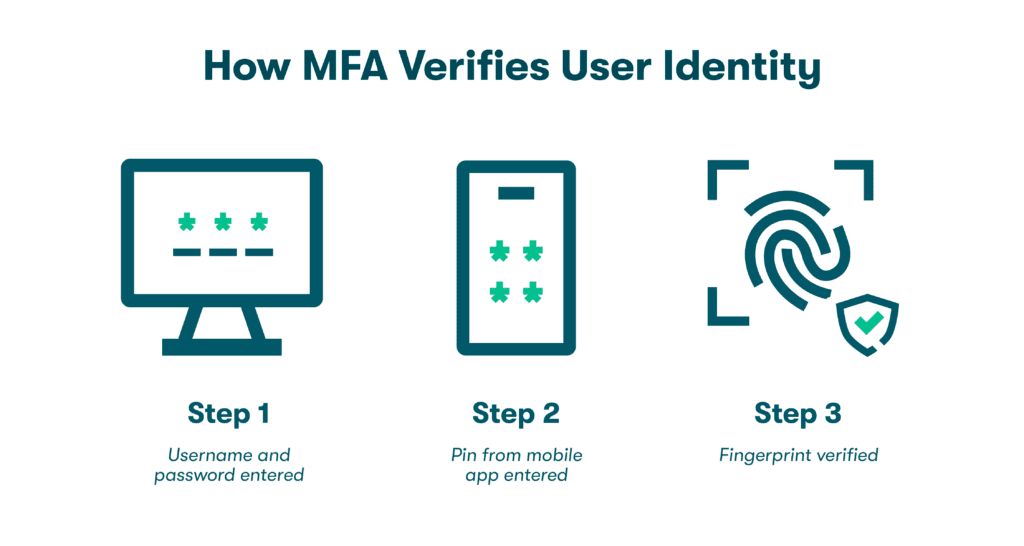
- Message authentication: Authentication is a cybersecurity concept based on verifying a person’s identity when they send and receive messages or log in to important accounts. 2-factor authentication (2FA) and multifactor authentication (MFA) use things like secret codes sent through apps, fingerprints, and facial recognition as authentication factors. Asymmetric encryption leverages private keys to support authentication. For example, when the holder of a private key sends a message or signs a document, the corresponding public key can be used to verify their identity.
- Tampering detection: If a hacker attempts to modify data in transit, the recipient’s private key will no longer be able to decode the message. This prevents the receiver from unknowingly accepting a corrupted message while providing a built-in alert mechanism when messages have been tampered with.
Asymmetric encryption vs. symmetric encryption
Symmetric encryption is an older technique that uses shorter key lengths (128, 192, or 256-bit) to support faster processing. Symmetric encryption uses the same key for both encryption and decryption rather than separate public and private keys.
Which is better?
Both symmetric and asymmetric encryption have their benefits. Determining which is better depends on the app and the level of security you need. Symmetric encryption is an established practice that can be used to transfer large files efficiently. Asymmetric encryption works more slowly but is considered safer due to the more complex algorithms and mismatched keys.
What is AES encryption?
The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is a secure form of symmetric encryption that divides data into blocks of 128 bits, then uses 14 rounds of encryption to scramble them beyond recognition. AES has been widely adopted for secure applications, including cloud security, hard drive encryption, and electronic payments. Dashlane Password Managers uses AES-256 encryption, widely accepted as the strongest symmetric encryption type available, to protect your passwords and private messages.
What is SSL/TLS?
Secure Socket Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) are important security protocols used to verify website authenticity during an SSL/TLS handshake. Steps of the asymmetric encryption process during a handshake include verifying the server's identity, agreeing on encryption methods, and generating asymmetric keys to secure the communication. Using SSL/TLS helps organizations keep their online transactions secure and their customers' data protected.
The best-in-class encryption used by Dashlane protects all customer data and metadata, not just passwords. Learn how AES-256 encryption and zero-knowledge architecture combine to keep your data secure and private from our CTO, Frederic Rivain: Putting Security First: How Dashlane Protects Your Data.
More examples of asymmetric encryption
It’s not difficult to find asymmetric encryption examples in our daily online activities. Since it was introduced over 20 years ago, asymmetric encryption has become an indispensable cybersecurity tool.
- E-commerce: Asymmetric encryption is commonly used in e-commerce transactions. When a buyer intends to make a purchase, the merchant (seller) sends them a public key, which they use to encrypt their payment information. Once the encrypted information is sent to the seller, they use their private key to decrypt the payment information and complete the transaction. Since only the merchant can access the private key, buyers can be confident that their payment information won’t be lost or stolen.
- Public key infrastructure (PKI): Many organizations rely on PKI to manage security processes through certificates. In the digital world, these certificates are used like passports or driver’s licenses that establish confidence in websites, transactions, and user identities. PKI uses public and private asymmetric keys generated by a Certificate Authority (CA) to encrypt and decrypt data so that it remains secure.
- Cryptocurrency: Bitcoin and other types of cryptocurrency use asymmetric encryption to protect their transactions. Public and private keys are used to verify the authenticity and sign off on all cryptocurrency transactions before they are permanently added to the blockchain. Asymmetric encryption ensures these transactions can’t be altered or tampered with and that only private key holders can access their own funds.
Crypto is the preferred currency of many cybercriminals, so it is important to protect your digital assets at all times. Find out why password managers are the perfect accessory for your crypto wallet.
- Digital signatures: Sending documents for online approval using DocuSign and other similar services became a welcome convenience during the pandemic. Document signatures are among many uses for digital signatures enabled by asymmetric keys. These signatures can also be used to detect unauthorized document modifications and preserve the security and integrity of online transactions.
The future of asymmetric encryption
The future of security in the hybrid workplace will bring many challenges as employers adapt to bring-your-own-device (BYOD) policies, limited IT access, and complex authentication practices. Encryption will remain an important tool for keeping employee and company data secure. As the hybrid workplace evolves, AES-256 and asymmetric encryption will help safeguard transaction integrity while preventing hacking and data breaches.
Dashlane provides intuitive, secure password generation features with encrypted vaults for password storage and sharing that prevent hackers from accessing your logins. Additional features like Password Health scores, 2FA, and Dark Web Monitoring keep your cybersecurity profile ahead of the curve.
Encryption is a powerful cybersecurity tool that most people know very little about.
Learn how to improve password health for yourself and your organization while boosting awareness of cybersecurity tools and best practices in A Practical Guide to Cybersecurity with a Password Manager.
References
- Thales, “A Brief History of Encryption (and Cryptography),” November 2022.
- Cloudflare, “What is asymmetric encryption?” 2023.
- Inspired eLearning, “Email Encryption – What Is It and How To Encrypt Your Emails,” April 2022.
- Key CDN, “HTTP vs HTTPS: The Difference Between HTTP and HTTPS,” June 2022.
- Dashlane, “A Deep Dive into Dashlane's Zero-Knowledge Security,” June 2022.
- Dashlane, “How to Conduct a Security Audit in Five Steps,” 2023.
- Microsoft, “What is: Multifactor Authentication,” 2023.
- Dashlane, “You Asked, A Hacker Answered: 7 Questions With Rachel Tobac,” October 2021.
- Trenton Systems, “Symmetric vs. Asymmetric Encryption: What's the Difference?” May 2021.
- SimpliLearn, “What Is AES Encryption and How Does It Work?” February 2023.
- Venafi, “What Are the Best Use Cases for Symmetric vs Asymmetric Encryption?” September 2022.
- Dashlane, “What is Encryption?” March 2019.
- Dashlane, “Putting Security First: How Dashlane Protects Your Data,” January 2023.
- KeyFactor, “What is PKI and How Does it Work?” 2023.
- Cyptopedia, “What Is Encryption? A Brief Overview,” April 2021.
- Dashlane, “The Future of Security in the Hybrid Workplace,” 2023.
- Dashlane, “A Practical Guide to Cybersecurity with a Password Manager,” 2023.
- Dashlane, “A Beginner’s Guide to Two-Factor Authentication,” August 2022.
Sign up to receive news and updates about Dashlane
Thanks! You're subscribed. Be on the lookout for updates straight to your inbox.
